The soft tissues of the body
Soft tissues are found throughout the body. There are many types of soft tissue,
including fat, muscle, fibrous tissue, blood vessels,
What the soft tissues do
Soft tissues:
- surround, support and connect organs and other body parts
- give shape and structure to the body
- protect organs
- move fluids, such as blood, from one part of the body to another
- store energy
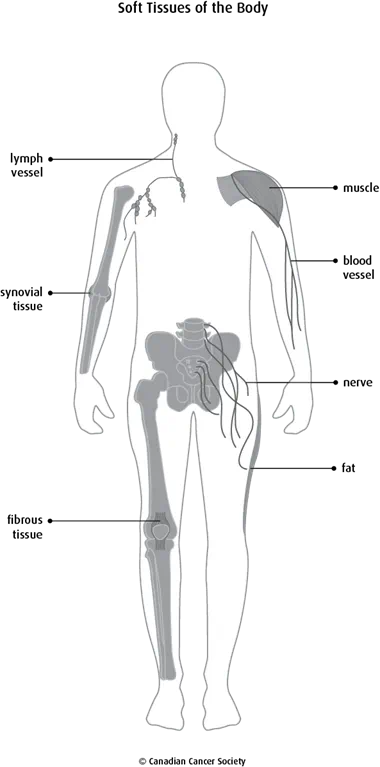
Types of soft tissue
There are different types of soft tissue found in the body.
Fat
Fat is a soft tissue made up of fat cells (adipocytes) that are packed tightly together. It may also be called fat tissue or adipose tissue. Fat is commonly found under the skin of the buttocks, hips, waist and abdomen. It also surrounds organs, such as the kidneys. Fat cushions the body, provides padding between organs and helps keep the body warm. The body also stores fat and uses it for energy when you need it.
Fibrous tissue
Fibrous tissue is
Muscle
There are 3 types of muscle – smooth muscle, skeletal muscle and cardiac (heart) muscle.
Smooth muscle works automatically without you thinking about it (involuntary muscle). It is found in the walls of the body’s hollow organs, such as the stomach, intestines, bladder, uterus and blood vessels. Smooth muscle allows organs to relax and get bigger (expand) or tighten and get smaller (contract).
Skeletal muscle is a type of muscle that you control to move your body (voluntary muscle). It is found mainly in muscles that attach to bones. Some skeletal muscles in the face attach to the skin. Skeletal muscle keeps the skeleton together and helps you stand upright. It also allows you to move different parts of your body, such as your arms and legs.
Cardiac muscle forms the walls of the heart and allows the heart to pump blood. Cardiac muscle works automatically without you controlling it.
Synovial tissue
Synovial tissue is thin and loose connective tissue that lines joints, such as elbows and knees. It is also found around tendons and fluid-filled sacs between bones and tendons (bursa). Synovial tissue makes synovial fluid, which is a thick liquid that allows areas to move easily.
Blood vessels
Blood vessels are long, elastic hollow tubes that are found throughout the body. Arteries, veins and capillaries are types of blood vessels. Blood travels through blood vessels and carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, waste and other products around the body.
Lymph vessels
Lymph vessels are small tubes like blood vessels that run throughout the
body. They contain
Nerves
Nerves are soft tissues that control all of the body’s functions and movements. Nerve tissue is made of 2 main types of cells – nerve cells (neurons) and glial cells (neuroglial cells). Nerve cells send messages (as electrical impulses) from one part of the body to another. Glial cells support the nerve cells. Most of the body’s nerve tissue is found in the brain and spinal cord, which is known as the central nervous system (CNS). Some nerve tissue is outside of the brain and spinal cord and called the peripheral nervous system. Nerve tissue is also called nervous tissue or neural tissue.
